This map from the 2017 annual report by the Water Authority of Jordan (WAJ) shows the different groundwater basins in Jordan. Except for 2 basins in the eastern and southeatern part of the country, all the groundwater basins are being over-exploited, with abstraction exceeding their safe yield. This is especially the case for the Zarqa basin and Azraq basin (serving the cities of Amman and Zarqa, at a rate of 188% and 290% of the safe yield resectively). This practice will without doubt affect the quality (risk of contamination and pollution) and the renewability of the water resources.
Additionally, this map clearly suggests that the groundwater basins should be considered as transboundary water resources, which are also being exploited across the border, like the Disi Aquifer.
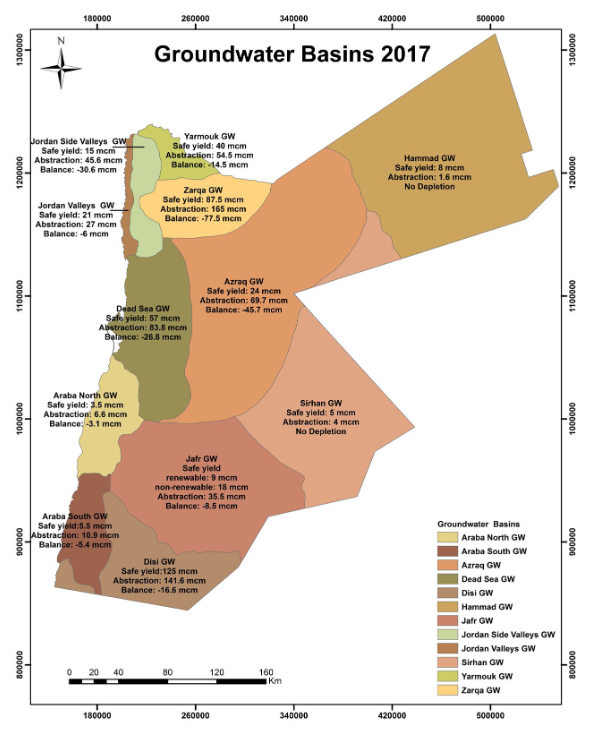 Jordan groundwater basins, from on Ministery of Water and Irrigation 2017
Jordan groundwater basins, from on Ministery of Water and Irrigation 2017
Source: Water Authority of Jordan (WAJ), Jordan Water Sector - Facts and Figures 2017.
A similar map below from an article in Nature (2019):
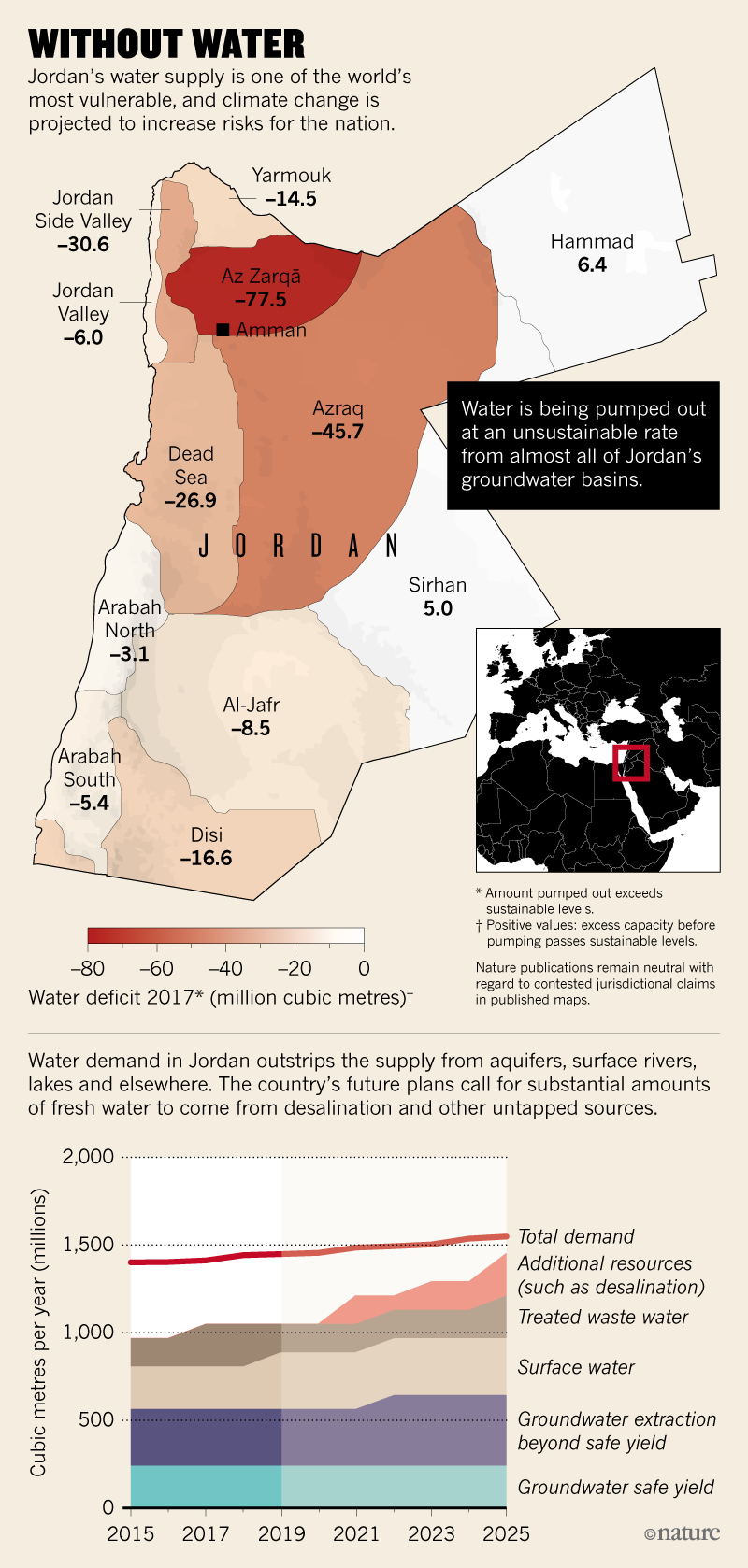 Jordan groundwater basins and water use, Nature 2019
Jordan groundwater basins and water use, Nature 2019
Source: Nature. 2019 (A land without water: the scramble to stop Jordan from running dry, https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-019-02600-w).

